Selection of chips is the core of success. Currently, NXP's NTAG NT3H1101 is widely used, with a high success rate and small size.
To achieve communication and power supply, antennas must be designed.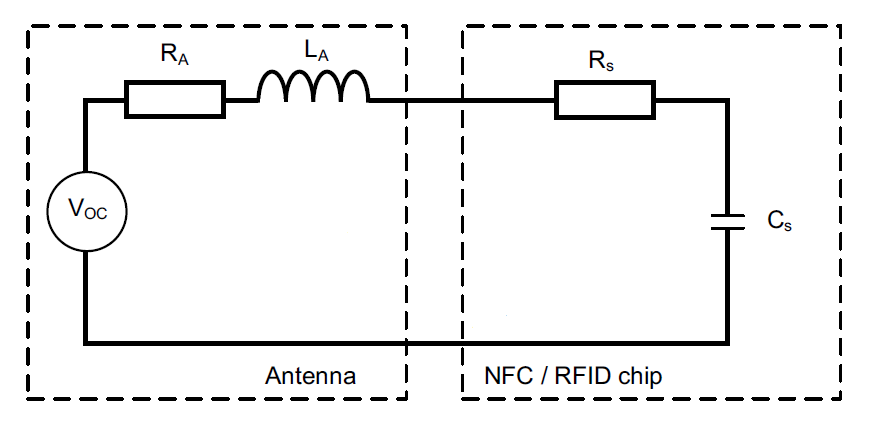
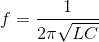
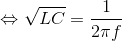
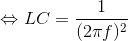

It is known that the RFID operating frequency is 13,56 MHz and the NT3H1101 tuning capacitor is 50 pF, then the calculation formula of the inductor L is:
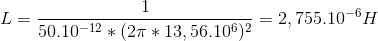
NXP provides gerber files for antennas built by its engineers and integrated into some of its products. The main advantage of this design is that it has been simulated, calibrated and fully optimized. download .
NXP recommends using a "Class 3", "Class 4", "Class 5" or "Class 6" antenna.
I decided to use a class 4 rectangular antenna, the perfect size for my business card, which should be located within the area defined below:
The layout of the inductive antenna on the PCB requires special attention*** because radio waves cannot pass through metal, so there must be no copper plane above or below the antenna.
√ Antenna layout design
√ Business card content layout
√PCB proofing
√Welding debugging

 Since the chip is very small, novices recommend SMT
Since the chip is very small, novices recommend SMT
This card can realize NFC communication with the mobile phone, open the website, connect to WiFi, add contacts, etc. It cannot be used as an M1 card.
The card type is Ultralight card, which is MF0 card.

All reference designs on this site are sourced from major semiconductor manufacturers or collected online for learning and research. The copyright belongs to the semiconductor manufacturer or the original author. If you believe that the reference design of this site infringes upon your relevant rights and interests, please send us a rights notice. As a neutral platform service provider, we will take measures to delete the relevant content in accordance with relevant laws after receiving the relevant notice from the rights holder. Please send relevant notifications to email: bbs_service@eeworld.com.cn.
It is your responsibility to test the circuit yourself and determine its suitability for you. EEWorld will not be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, consequential or punitive damages arising from any cause or anything connected to any reference design used.
Supported by EEWorld Datasheet