What is the difference between a microcontroller and a microprocessor?
Source: InternetPublisher:newrudeman Keywords: Microcontroller microprocessor Updated: 2025/01/10
Microprocessor vs Microcontroller, Often in schools and colleges we find it difficult to spot the difference between a microcontroller and a microprocessor.
Well, these two complex terms are the soul and heart of programmable electronics. ELE Times always understands the need and importance of having a good understanding of the basics of electronics. Hence, we have tried to explain to our readers what are Microcontroller and Microprocessor.
Three main differences between microcontrollers and microprocessors
Cost: Generally, microcontrollers cost less than microprocessors. Microprocessors are usually used in more expensive devices. They are also significantly more complex, as they are designed to perform a variety of computing tasks, while microcontrollers usually perform specialized functions. With a microcontroller, engineers write and compile code for a specific application and upload it to the microcontroller, which contains all the computing functions and components necessary to execute the code.
speed:
When it comes to clock speed, there is a significant difference. This has to do with the idea that microcontrollers are used to handle specific tasks or applications, while microprocessors are used for more complex, robust, and unpredictable computing tasks. This means using just the right amount of speed and power to get the job done.
- No more, no less. Thus, many microprocessors have clock speeds of up to 4 GHz, while microcontrollers can run at slower speeds of 200 MHz or less.
Power consumption:
One of the main advantages associated with microcontrollers is their low power consumption. Computer processors that perform specialized tasks require lower speeds and, therefore, lower power consumption than processors with greater computing power. Power consumption plays an important role in implementing a design: processors that consume a lot of power may need to be plugged into or supported by an external power supply, while processors that consume limited power may only be powered by a small battery for a long time.
What is a Microcontroller?
A microcontroller (sometimes called an MCU or microcontroller unit) is a single integrated circuit (IC) that is usually used in a specific application and is designed to achieve certain tasks. Products and equipment that must be automatically controlled in certain situations, such as appliances, power tools, automotive engine control systems, and computers are good examples, but the scope of microcontrollers goes far beyond these applications.
Essentially, a microcontroller collects input, processes this information, and outputs a specific action based on the information collected. Microcontrollers typically run at relatively low speeds, around 1MHz to 200MHz.
MHz range and need to be designed to consume less power because they are embedded in other devices that may have larger power consumption in other areas.
What is a Microprocessor?
A microprocessor is an electronic component that a computer uses to do its work. It is a central processing unit on a single integrated circuit chip that contains millions of very small components, including transistors, resistors, and diodes, working together. Some 20th century microprocessors required several chips. Microprocessors help do everything from controlling elevators to searching the web. Everything a computer does is described by the instructions of a computer program, and a microprocessor executes these instructions millions of times per second.

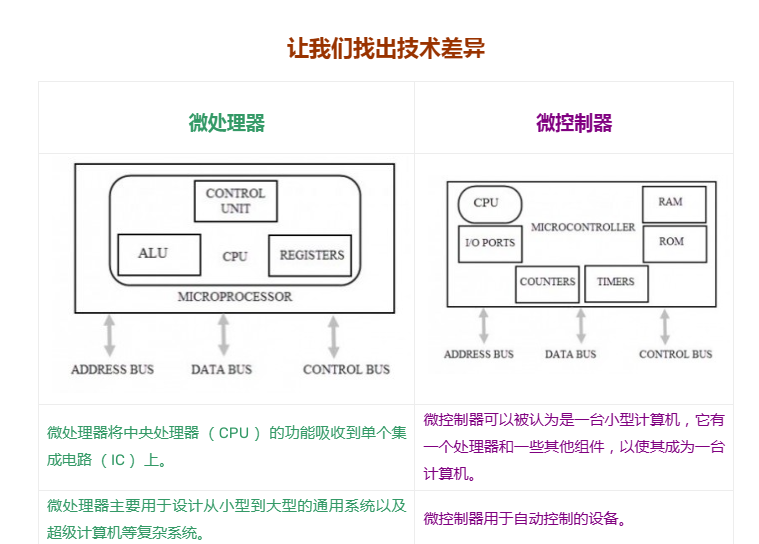
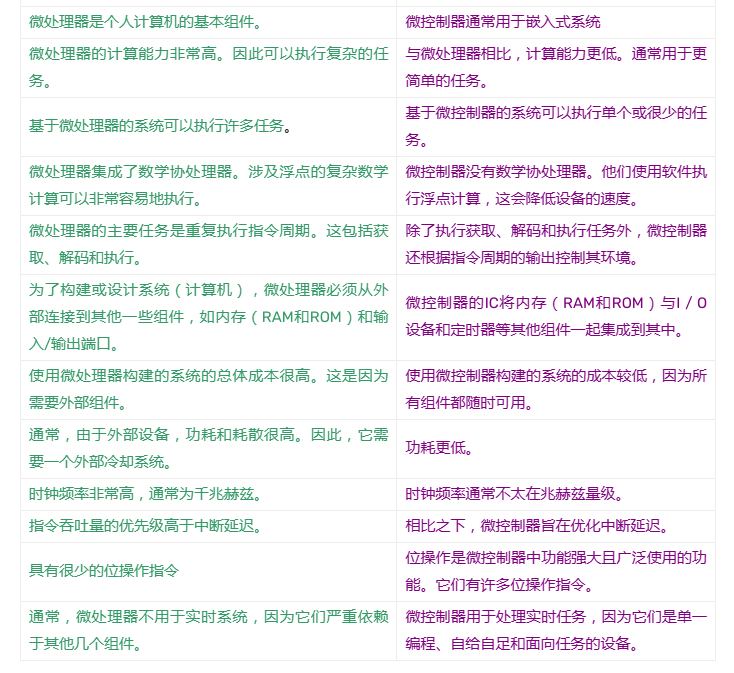
Ultimately, microcontrollers and microprocessors are different ways of organizing and optimizing computing systems based on the CPU. Microcontrollers put the CPU and all peripherals on the same chip, while microprocessors have a more powerful CPU on a single chip connected to external peripherals. Microcontrollers are optimized to perform specialized, low-power applications (ideal for embedded systems), while microprocessors are more useful for general-purpose computing applications that require more complex and general-purpose computing operations.
- Make an alcohol tester based on 8051 microcontroller
- Introduction to the use of UnoArduSim
- How to design a pet activity tracker using XIAO BLE Sense
- Homemade bidirectional reversible length measuring device for rubber tubes
- Circuit diagram of multifunctional digital clock
- Sample and hold amplifier AD9101 interface circuit
- AD8351 and SAW filter interface circuit
- How to design an AirPlay speaker using Raspberry Pi Zero
- How to make a numeric keyboard using XIAO RP2040
- Ultrasonic anti-theft alarm designed based on microcontroller and HC-SR04
- Indoor unit remote control receiving and display circuit
- Rice cooker operation display circuit
- Detection parts and data of reset circuit
- TMP86C807MG chip internal structure diagram
- The structure of Hisense KFR-25GW-06BP inverter air conditioner outdoor unit microprocessor control circuit
- μPD550C (TV) 4-bit single-chip microprocessor circuit
- MN15245SAY (television) remote control microprocessor circuit
- M9082 (TV) infrared remote control transmitter microprocessor circuit
- Microprocessor Teletypewriter Circuit
- Microprocessor Interrupt Generator Circuit







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号