How to judge the quality of insulation of low-voltage motors?
Source: InternetPublisher:Lemontree Keywords: Electric motor insulation low voltage electric motor Updated: 2025/03/04
The insulation condition of low-voltage motors below (500) volts is generally checked with a 500-volt insulation megger. If there is no insulation tester and the insulation condition of the motor needs to be determined quickly, a signal light can be used for a rough judgment.
Judgment method:
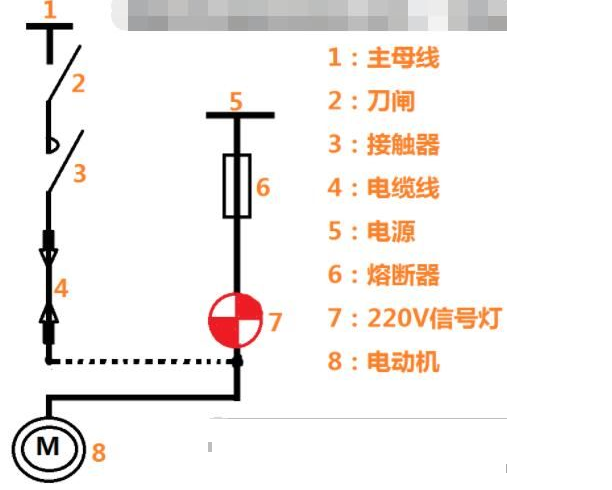
Connect a 220V signal lamp according to the diagram, then power it on and make the following judgments:
1. If the light bulb is off, it means the insulation of the motor is good and can be put into operation;
2. If the filament of the bulb turns red, it means there is leakage and the insulation of the motor is slightly damaged. If the production cannot be interrupted and the protection device is sensitive and reliable, the motor can be used temporarily;
3. If the light bulb glows normally or very brightly, it means that the insulation of the motor is seriously damaged and cannot be used. Otherwise, a short circuit and burnout accident may occur.
Similarly, the dotted line indicates that the insulation of the cable can be checked.
- How to judge the quality of insulation of low-voltage motors?
- A simple magnetic switch circuit sharing
- What is a 4-pin PWM header? How do 4-pin PWM fans work?
- Analysis of the working principle of car garage door lights
- How can we make the robot move precisely on a predefined path?
- What is a RADAX motor?
- A small improvement to the temperature and water level indicator alarm
- JDB-LQ-TQ/2 motor full voltage starting circuit
- An experimental model of an infrared radio alarm
- Car audio system anti-theft circuit
- fire smoke control circuit
- Car window control circuit
- PLC chain alarm control circuit used in production process
- Automatic door detection control circuit
- Microwave heating component control circuit schematic diagram
- Steam iron temperature detection control circuit
- Taifu DK2-25 rice cooker temperature detection control circuit
- Micro DC motor steady speed control circuit b
- Inverter brightness control circuit
- Wide input range non-synchronous voltage mode control circuit








 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号