What is a pure resistance circuit? What is a pure resistance AC circuit?
Source: InternetPublisher:走马观花 Keywords: Resistors resistor circuits Updated: 2025/01/24
What is a purely resistive circuit? A purely resistive circuit is one in which the inductance is so small that, at its typical frequency, its reactance is negligible compared to its resistance. Furthermore, in a purely resistive circuit, the entirety of the applied voltage is used to overcome the ohmic resistance of the circuit itself. Furthermore, another name for a purely resistive circuit is a non-inductive circuit.
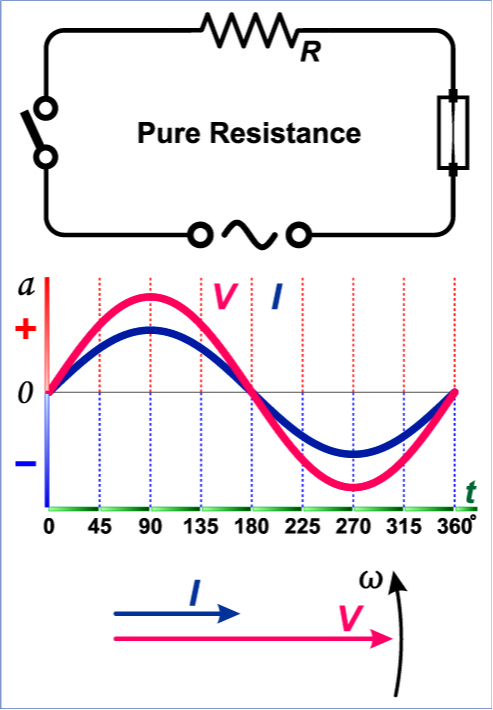
Furthermore, in a purely resistive circuit, the phase angle between the current and voltage is zero. Furthermore, if we were to express the instantaneous current and the instantaneous applied voltage for a typical purely resistive circuit, it would show that the supplied voltage and current are indeed in phase with each other.
Furthermore, if we examine a graphical representation of the same circuit, we can see from its power curve that no part of the power cycle ever goes negative at any time. Therefore, in a purely resistive circuit, the power is never zero. Furthermore, this is due to the fact that the instantaneous values of the current and voltage are always either negative or positive. Furthermore, the power cycle frequency of a purely resistive circuit is twice the frequency of the current and voltage waves.
The relationship between current and voltage dictates the type of resistor used in a circuit
What is a pure resistance AC circuit?
A circuit that contains only pure resistance (Ohms) in an AC circuit is called a pure resistance AC circuit. From a technical point of view, this circuit does not contain capacitance or inductance. The AC voltage and current move synchronously forward and backward in either direction of the circuit. Therefore, the AC voltage and current take the shape of a sine wave, hence it is called a sinusoidal waveform.
In these circuits, the resistor consumes power while the phase of the current and voltage remains constant. The current and voltage reach their maximum values at the same time. It is important to note that a resistor is a passive component, which neither generates nor consumes electrical energy. So, what effect does a resistor have on power in a purely resistive circuit? It converts available energy into heat.
In an AC circuit, the ratio of current to voltage depends on the phase angle, phase difference, and power frequency. In addition, the resistance value of a resistor will remain constant regardless of the power frequency.
- Why do we need a MOSFET gate resistor? MOSFET Gate Resistor Placement
- How are diodes made using semiconductors?
- Analysis of the basic principle of measuring resistance by bridge method
- What are the types of commonly used batteries?
- How to calculate the value of capacitors in parallel?
- Basic characteristics/working principles and application circuits of tunnel diodes
- How to build a drag racing timer circuit using a 7-segment display and discrete components
- LED lights that “drain” battery power
- Purpose and composition of amplifier circuit: low frequency voltage amplifier amplifier circuit
- FL52C4 induction electronic greeter
- Calculate amplification, input resistance, and output resistance circuits
- Positive temperature sensor and coefficient resistor circuit diagram
- Compensation resistor circuit diagram
- Monostable photoresistor circuit with self-adjusting trigger level
- OPT209 external feedback resistor circuit
- 555 square wave oscillation circuit
- 555 photo exposure timer circuit diagram
- Introducing the CD4013 washing machine timer circuit diagram
- Simple level conversion circuit diagram
- 555 electronic guide speaker circuit diagram for blind people







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号