Many applications require the capability to automatically disconnect power from an operating circuit. Such applications include thermal shutdown of high-voltage power supplies in radar and X-ray systems, shutdown to limit inrush current during power-up or hot-swapping of pc cards, and shutdown to ensure that a card is properly seated before power is applied. In general, a power fault system will keep the power off following the system fault, until it is deliberately reset.
Figure 1 is a flexible circuit that limits current or removes power in response to a command from the user or other fault-indicating signal. It accommodates manual-reset (MR), over-temperature, and interlock-switch inputs. U1, for instance, is a circuit-breaker IC designed to offer protection in hot-swap applications. Residing on either the backplane/host side or the removable-card/remote-device side of the backplane connectors, it guards against start-up faults when a card or board is inserted into a rack or host with the main power supply turned on.
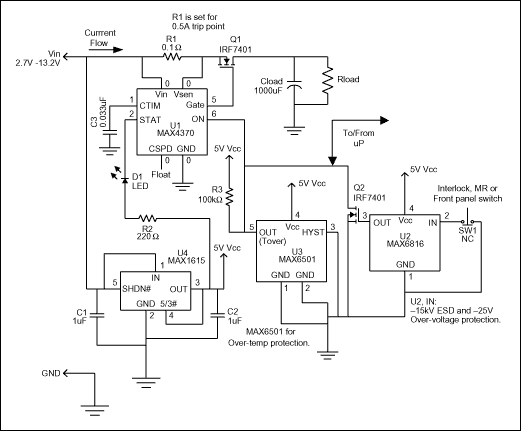
Figure 1. This circuit provides general over-current and over-temperature protection.
All reference designs on this site are sourced from major semiconductor manufacturers or collected online for learning and research. The copyright belongs to the semiconductor manufacturer or the original author. If you believe that the reference design of this site infringes upon your relevant rights and interests, please send us a rights notice. As a neutral platform service provider, we will take measures to delete the relevant content in accordance with relevant laws after receiving the relevant notice from the rights holder. Please send relevant notifications to email: bbs_service@eeworld.com.cn.
It is your responsibility to test the circuit yourself and determine its suitability for you. EEWorld will not be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, consequential or punitive damages arising from any cause or anything connected to any reference design used.
Supported by EEWorld Datasheet