Types and specifications of optocoupler ICs
Source: InternetPublisher:闪电杰克 Keywords: Optical coupler optical components Updated: 2025/02/18
Optocouplers may not sound like something related to electronics, but they are an important component in providing isolation between different circuit blocks. Optocoupler ICs integrate optical components that work like simple switches and are widely used in different circuits. They are also ideal for use in feedback loops between different circuit blocks, especially where isolation is required. Some optocouplers are also designed to provide switches with high data rates.
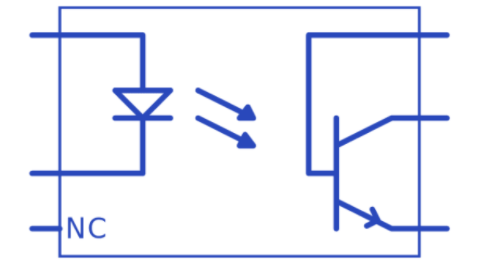
1. What is an optocoupler?
Quite simply, an optocoupler integrates an infrared LED with a photodetector (usually a phototransistor), acting like a light switch. When the LED receives an input signal, the LED lights up and supplies photons to the base of the phototransistor. The phototransistor then turns on, allowing current to flow through the connected circuit. The LED may operate at a different level than the internal phototransistor, allowing for some isolation between the two signal levels. This is a way to conduct low-voltage signals into high-voltage circuit blocks without using an amplifier.
Optocouplers are great at providing electrical isolation between different circuit blocks without conducting certain forms of EMI between the different circuit blocks, but that is not to say they solve all noise problems. The advantage of using optocouplers is that the isolation provided does isolate the systems at different voltages, which has the benefit of suppressing ground loop noise from both parts of the system.
Types of Optocoupler ICs
In addition to phototransistors, optocouplers can use other switching elements. Here are some types of optocoupler IC types that can be found in the electronics market:
1. Triac: Optocoupler ICs with triac as detector are used in systems requiring high output voltage/current. They have a slower response speed and are best suited for high voltage DC systems that require high current output.
2. Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCR): These optocouplers also offer high gain, similar to triacs. However, they also operate slowly and are also best suited for medium voltage/current DC systems.
3. Photodiode: Optocouplers with photodiodes as detectors are common in circuit systems that require fast switching. These components can be used when LEDs are switched by digital pulse streams or AC signals. Photodiodes will provide a very low output-to-input current transfer ratio compared to a typical phototransistor IC.
4. Darlington Phototransistor: These optocouplers are also useful because of their high gain and have the highest output to input current transfer ratio.
5. Photoresistors: They are less commonly used because they still conduct in the OFF state. Also, their output to input current transfer ratio is low.
Important optocoupler IC specifications
When choosing an optocoupler IC, you may want to first understand the packaging style of the optocoupler IC. They are usually available in through-hole DIP packages or surface mount components. However, there are some important specifications that you should check when choosing an optocoupler IC:
1. LED forward voltage and trigger current. This tells you how to power the input LED to ensure it lights up and provides the desired switching behavior. In an optocoupler designed to switch with a square wave or PWM signal, the forward peak current required to trigger the switch depends on the pulse width of the signal in the on state. Shorter pulses require larger peak signal currents to force triggering.
2. The ratio of output to input current. This tells you the current transfer between the two ends of the optocoupler, and it is important to note that this depends on the absolute maximum collector-emitter voltage of the phototransistor optocoupler.
3. Forward voltage vs. forward current curve. This specification has the same meaning as for standard LEDs, but do not confuse it with the trigger current.
4. Temperature variation. These specifications are very important for power systems because they may reach high temperatures during operation.
5. Safety rating and IEC/UL certification. If you are designing for a power system or data transmission in a high voltage environment near AC power, IEC is an important standard to pay attention to to ensure that high transient voltages can be withstood.
6. Data rate or switching speed. Although the switching speed or frequency can also be specified, if it is an optocoupler chip used in data networks, the maximum data rate is usually specified.
- Summing amplifier circuit diagram analysis
- How to convert an inverting amplifier into a summing amplifier?
- What is a photocoupler and how to select and use one?
- What is a FinFET? What are the advantages and disadvantages of FinFET?
- Voltage divider circuit calculation formula, where to find the voltage divider circuit?
- An article explains the working principle of the Wheatstone bridge
- How to read resistor color codes? Resistor color codes illustrated
- How does sand become chips?
- What types of power field effect tubes are there? Selection criteria for power field effect tubes
- How does RCCB work?
- Lighting delay light off circuit using optocoupler b
- Simple AC relay using two optocouplers
- Chopper circuit using optocoupler
- Optocouplers and discrete Schmitt triggers used to drive 54/74 TIL circuits
- Optocoupler TIL120/TIL121 connection equivalent circuit
- TIL300/TIL300A precision linear optocoupler application circuit
- TIL118-1/TIL118-2/TIL118-3 optical coupler circuit
- OPI8012 to OP8015 type optocoupler/optical isolation circuit
- LH1056 type high voltage solid relay optocoupler circuit
- HCPL2052 type optocoupler/optical isolation circuit-schematic diagram







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号