This application note describes how LEDs, including WLEDs, work. The note also explains how to drive them in battery-powered LED applications, including lithium-ion (Li+ or Li-ion), nickel-cadmium (NiCd), and nickel metal-hydride (NiMH) rechargeable handheld devices where power consumption is important. LED brightness matching and the value of series vs. parallel LEDs are discussed. Application information is also presented for several LED drivers that can efficiently drive and control LEDs.
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are the solid-state, highly reliable, efficient counterparts of the evacuated tungsten-filament light bulb. Epitaxial material based on gallium arsenide phosphide (GaAsP) produces red, green, or yellow outputs (Figure 1). Material based on indium gallium nitrate (InGaN) produces blue or white outputs (Figure 2). Different chemistries also produce different electrical characteristics.
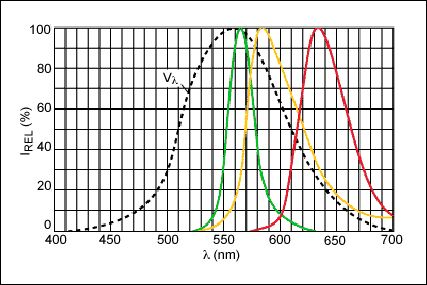
Figure 1. Relative spectral response of red, green, and yellow diodes (IF = 2mA, TA = +25°C).
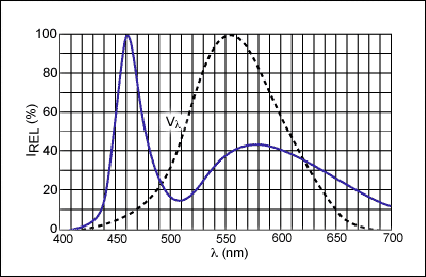
Figure 2. Relative spectral response of white diodes (IF = 20mA, TA = +25°C).
In Figures 1 and 2, the curve Vλ represents the standard response of a human eye. To obtain white light, a blue emitter is covered with material that emits yellow light when stimulated by blue light. The eye interprets the output as white and creates the spectral response of Figure 2.
All reference designs on this site are sourced from major semiconductor manufacturers or collected online for learning and research. The copyright belongs to the semiconductor manufacturer or the original author. If you believe that the reference design of this site infringes upon your relevant rights and interests, please send us a rights notice. As a neutral platform service provider, we will take measures to delete the relevant content in accordance with relevant laws after receiving the relevant notice from the rights holder. Please send relevant notifications to email: bbs_service@eeworld.com.cn.
It is your responsibility to test the circuit yourself and determine its suitability for you. EEWorld will not be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, consequential or punitive damages arising from any cause or anything connected to any reference design used.
Supported by EEWorld Datasheet