What is the difference between MOSFET and BJT? Which one is better between MOSFET and BJT?
Source: InternetPublisher:supremeOne Keywords: MOSFET FET Field Effect Transistor Updated: 2025/02/11
Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) and bipolar junction transistor (BJT) are two types of transistors that come in different packages, and people who are not familiar with electronics often have trouble deciding which one they should use in their development projects. Engineers explain that although both MOSFET and BJT are transistors, they work differently and exhibit different behaviors, so they are used differently.
1. What is MOSFET?
A Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is a type of Field Effect Transistor (FET) consisting of three terminals - Gate, Source and Drain. In a MOSFET, the drain is controlled by the voltage at the gate terminal, so the MOSFET is a voltage controlled device. The voltage applied to the gate controls the amount of current that flows into the drain. There are two types of MOSFETs, "p-channel" and "n-channel". Both types can be in either enhancement or depletion mode (see Figure 1). This means there are four different types of MOSFETs in total.
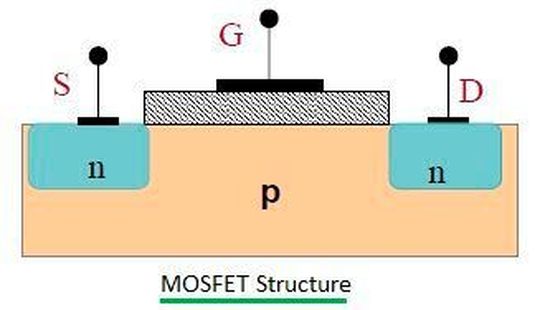
In a p-channel MOSFET, the source and drain terminals are made of p-type semiconductors. Similarly, in an n-channel MOSFET, the source and drain terminals are made of n-type semiconductors. The gate terminal itself is made of metal and is separated from the source and drain terminals using a metal oxide. This level of insulation stems from low power dissipation and is the main advantage of this type of transistor. This often sees MOSFETs used in low-power devices or as a building block to reduce power consumption.
Depletion Mode: When the gate voltage is low, the channel exhibits maximum conductance. As the gate voltage is positive or negative, the channel conductivity decreases.
Enhancement Mode: When the voltage at the gate terminal is low, the device does not conduct unless more voltage is applied to the gate terminal.
2. What is BJT?
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a current-driven device (in contrast, a MOSFET is voltage-driven) that is widely used as an amplifier, oscillator, or switch, etc. A BJT has three pins (base, collector, and emitter) and two junctions: a p-junction and an n-junction.
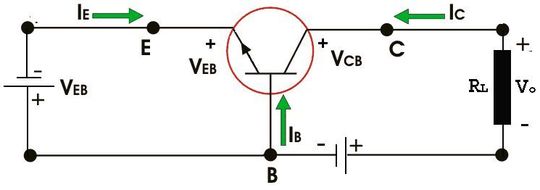
There are two types of BJTs - PNP and NPN. Each type has a large collector component and a large emitter component that are doped in the same way. Between these structures is a small layer of other dopants called the "base." Current flows into the collector of a PNP and out of the emitter. In an NPN, the polarity is reversed, with current flowing into the emitter and out of the collector. In either case, the direction of current in the base is the same as the collector.
Fundamentally, the operation of a BJT transistor is determined by the current at its base terminal. For example, a small base current equals a small collector current. The output current of a BJT is always equal to the input current multiplied by a factor called "gain", which is usually 10-20 times the base current.
3. What is the difference between MOSFET and BJT?

There are many differences between MOSFET and BJT:
(1) MOSFET (voltage controlled) is a metal oxide semiconductor, while BJT (current controlled) is a bipolar junction transistor.
(2) Although both have three terminals, they are different. A MOSFET has a source, drain, and gate, while a BJT has a base, emitter, and collector.
(3) MOSFETs are ideal for high-power applications, while BJTs are more commonly used in low-current applications.
(4) A BJT depends on the current at its base terminal, whereas a MOSFET depends on the voltage at the oxide-insulated gate electrode.
(5) The structure of MOSFET is inherently more complex than that of BJT.
Which is better, MOSFET or BJT?
Both MOSFETs and BJTs have unique characteristics and their own advantages and disadvantages. However, we cannot say which one is "better" because the question is very subjective. There is no straight and clear answer to this question.
When choosing which to use in your project, there are many different factors that must be considered in order to make a decision. These include power levels, drive voltage, efficiency, cost, and switching speed, to name a few - this is where understanding your project can really help!
In general, MOSFETs are generally more efficient in power supplies. For example, in a battery-powered device with a variable load and limited power supply, using a BJT would be a bad idea. However, if the BJT is used to power something with a predictable current draw, such as an LED, then this is fine because the base-emitter current can be set to a fraction of the LED current for better efficiency.
- What is a photocoupler and how to select and use one?
- Why do we need a MOSFET gate resistor? MOSFET Gate Resistor Placement
- How are diodes made using semiconductors?
- What factors are related to the hysteresis loss of the transformer? Can the hysteresis loss be reduced?
- How does sand become chips?
- What types of power field effect tubes are there? Selection criteria for power field effect tubes
- How does RCCB work?
- How to build a triangle wave generator using an op amp and discrete components
- Tutorial on building a NOT gate using BJT transistors
- LED Night Light
- 175MHz high frequency power amplifier circuit composed of field effect transistors
- Headphone circuit based on field effect transistor as silencer
- Wide dynamic range mixing circuit
- Balanced mixing circuit composed of two double-gate field effect transistors
- MOSFET gate depression test oscillator circuit diagram
- Motor drive circuit using P and N channel FETs
- Four-phase drive circuit
- Class A FET amplifier power supply circuit diagram
- FET FM wireless microphone circuit
- Differential Input FET Buffered Current Source Circuit Diagram







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号