Semiconductor fuse symbol diagram, semiconductor fuse working principle, how to select semiconductor fuse
Source: InternetPublisher:天天都吃好吃的 Keywords: Semiconductors fuses protective devices Updated: 2025/03/04
A fuse is an electrical protection device that is used to protect an electrical circuit from overload, overcurrent, etc. Thomas Alva Edison invented an electrical fuse in 1890. These devices come in different sizes, however, they all serve the same purpose. Fuses are classified into two types namely AC fuses and DC fuses. Therefore, this article discusses one type of DC fuse i.e. semiconductor fuse, suitable for applications.
What is a semiconductor fuse?
Semiconductor fuses are a type of current protection device, also known as high-speed fuses or ultra-fast fuses or rectifier fuses. They are mainly used to limit large currents and protect sensitive semiconductor components such as thyristors, power supplies, SCRs, rectifiers, diodes, etc. These fuses are very fast-acting current limiting devices that provide peak allowable currents and low melting point integral values. Typically, these fuses range from 125 to 2,100 V and are available in a variety of sizes and shapes. The semiconductor fuse symbol is shown below.
Semiconductor fuse symbol
The structure of semiconductor fuse
The semiconductor fuse structure is shown below, which has a fuse element, which is surrounded by a filler and surrounded by a fuse body. The fuse element inside this fuse is made of fine silver that is resistant to oxidants. The melting point of the silver material is 960°C, which can resist the maximum operating temperature of the limiter. The fuse body is made of heat-stable alumina ceramic.
Semiconductor fuses are also called high breaking capacity or current limiting fuses. Sometimes, these are called ultra-fast fuses or rectifiers. The time required to melt the fuse element is called the pre-arcing time.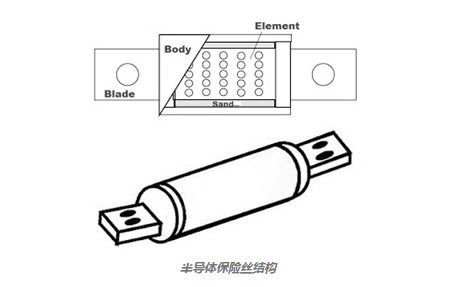
Semiconductor fuse structure
Working Principle of Semiconductor Fuse
The working principle of semiconductor fuses is to allow the current supplied to the circuit from the power supply to power the circuit correctly. If a short circuit or overload occurs, the current supply may break the filament in the fuse and cut off the power connection in the entire circuit. Therefore, when the limit of the predefined current is reached, the fuse will open the circuit. These fuses will replace AC and DC fuses in many fields. Any overload current will cause the fuse to open the circuit and avoid circuit damage. These fuses are generally used to protect semiconductor components such as transistors, integrated circuits, diodes, etc.
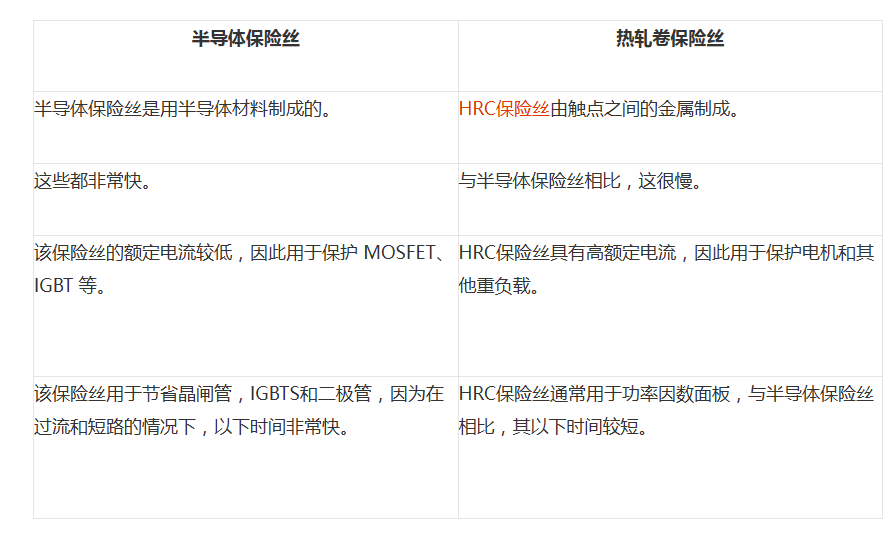
Semiconductor Fuses and Hot-Rolled Coil Fuse Cutouts
The differences between semiconductor fuses and HRC fuses are discussed below.
Semiconductor Fuse Selection
The selection of semiconductor fuses can be made according to the following requirements.
Under normal operating conditions, this fuse should continuously carry the rated current of the equipment.
The I2t fuse value must be low compared to the rated I2t of the device so that the fuse blows before the device.
The fuse must be able to withstand the voltage that appears across it after the arc has extinguished.
The voltage of the peak arc must be low compared to the device peak voltage rating so that the device is not damaged.
The selection of this fuse depends mainly on practical requirements such as I²t rating, rated voltage, braking capability, size and rating of fuse holder, fuse classes gS and gR, aR and
gPV, physical limitations within the design or on site, low current rating, range of ratings available for each package type, etc.
Semiconductor fuse selection for soft starters must be done very carefully to protect the thyristors used in each soft starter and the continuous current rating.
Semiconductor Fuse Characteristics
The current semiconductor fuse characteristics are shown below. We know that fast-blow fuses are used to protect semiconductor devices. When this fuse is connected in series to a semiconductor device, it will disconnect once the current increases to its rated value.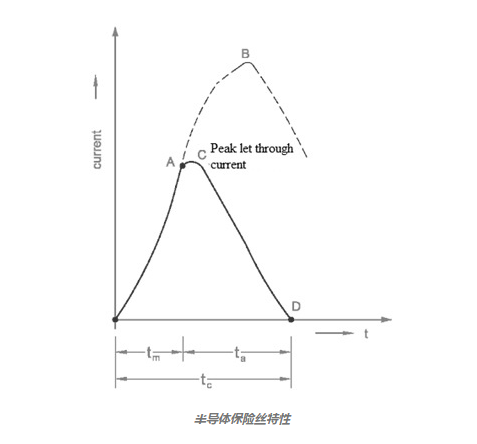
Semiconductor Fuse Characteristics
When this fuse is not used in the circuit, the fault current will increase to point "B". As the fuse current increases, the temperature also increases. Similarly, when a fuse is used in the circuit, the fault current increases to t =
tm. Therefore, once the fuse opens at time t = tm, a spark will occur across the fuse.
The fault current increases to point A, which is called the peak pass-through allowable current, represented by point C. At point C, when the arc resistance increases, the fault current decreases.
At point D, the arc decreases and the fault current becomes zero at this point. tc (fault clearing time) is the addition of tm (melting time) and ta (arcing time) of the fuse, such as tc = tm + ta.
The voltage across the fuse during the entire arcing time is called the arc voltage or recovery voltage. Therefore, it is important to note that the fuse I^2t rating is always lower than the SCR I^2t rating.
What is the HSN code for semiconductor fuses?
Generally, the Harmonized System of Nomenclature or HSN code is developed by the WCO (World Customs Organization) to classify various goods. It is a 6-digit code that is generally used for different commodities. However, some countries use 8-
digit codes to sub-classify commodities. So, the HSN code for semiconductor fuses is 853610.
How to check semiconductor fuse?
Semiconductor fuses can be checked by selecting the fuse, isolating the capacitor, forcing a voltage to the fuse, and measuring the current demand of the fuse. The first current level specifies an uninterrupted fuse, while the second current level specifies a blown fuse.
Application/Use
The applications or uses of semiconductor fuses include the following.
Semiconductor fuse applications mainly include semiconductor device protection in power rectifiers, AC and DC motor drives, converters, soft starters, photovoltaic inverters, solid-state relays, welding inverters, etc.
These fuses are widely used in power electronics applications such as variable frequency drives, thyristor DC drives and uninterruptible power supplies.
This fuse is used to protect the device from high current.
These fuses are used in different applications like short circuit protection, overvoltage, overcurrent, slew rate control, TSD (thermal shutdown), and RCB (reverse current blocking).
This fuse is a very fast conventional fuse that protects semiconductor devices from damage.
This fuse is typically used with large semiconductor devices rated for switching currents of 100A or more.
So, this is all about the overview of Semiconductor Fuses –
Use Applications. These protection devices help in protecting semiconductor devices from short circuits. Semiconductor fuses have ultra-fast action characteristics developed specifically for semiconductor power device protection. Here is a question for you, what is an HRC fuse?
- Analysis of Operational Amplifier Differentiator Circuit
- The unidirectional conduction current of the diode, the diode and its common uses
- How do pull-up resistors work? How do I choose a pull-up resistor value?
- What is a pure resistance circuit? What is a pure resistance AC circuit?
- What does a rectifier do? What is the process of rectification?
- Capacitance detection circuit configuration, how to deal with low frequency and high frequency noise?
- What are the types of commonly used batteries?
- What are the classifications of filters?
- Why Do Amplifier Fuses Blow? How Do You Prevent Amplifier Fuses from Blowing?
- TL494 pin functions/configuration/ratings/operating conditions/layout diagram
- Technical Analysis of Semiconductor Wide Bandgap
- Amid the Sino-U.S. trade war, U.S. semiconductor manufacturers begin to relocate abroad
- Protect zero circuit
- Fuse blown centralized monitoring circuit 3
- Fuse blown sound and light alarm circuit 5
- Fuse blown indication circuit 2
- Harmonic current phase failure protection circuit 2b
- 3W semiconductor amplifier circuit
- DC low voltage fuse blown indication circuit
- Electronic ballast protection device circuit








 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号