TVS diode selection guide, TVS diode selection considerations
Source: InternetPublisher:两手空空 Keywords: TVS diodes transient voltage suppressors Updated: 2025/03/07
TVS diode working principle
TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressors) diodes, also known as avalanche breakdown diodes, are devices made of a single PN junction or multiple PN junctions integrated using semiconductor technology. TVS diodes are divided into unidirectional and bidirectional. Unidirectional TVS diodes are generally used in DC power supply circuits, and bidirectional TVS diodes are used in circuits with alternating voltages. When applied to DC circuits, unidirectional TVS diodes are reversely connected in parallel in the circuit. When the circuit is working normally, the TVS diode is in the cut-off state (high resistance state) and does not affect the normal operation of the circuit. When an abnormal overvoltage occurs in the circuit and reaches the breakdown voltage of the TVS diode, the TVS diode quickly changes from a high resistance state to a low resistance state, discharging the instantaneous overcurrent caused by the abnormal overvoltage to the ground, while clamping the abnormal overvoltage at a lower level, thereby protecting the subsequent circuit from damage by the abnormal overvoltage. When the abnormal overvoltage disappears, the resistance of the TVS diode returns to a high resistance state.
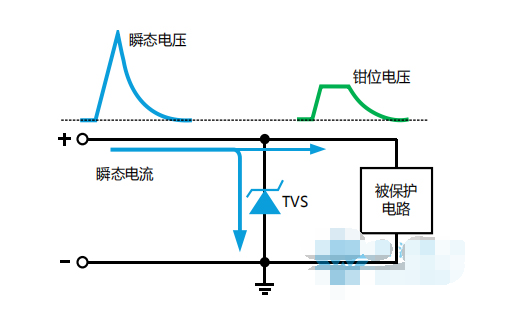
TVS diode selection method
1. First determine the maximum DC or continuous operating voltage of the protected circuit, the rated standard voltage of the circuit and the "high end" tolerance.
2. The rated reverse shutdown voltage VWM of TVS should be greater than or equal to the maximum operating voltage of the protected circuit. If the selected VWM is too low, the device may enter an avalanche state or the reverse leakage current may be too large, affecting the normal operation of the circuit.
3. The maximum clamping voltage VC of TVS should be less than the damage voltage of the protected circuit.
4. The maximum peak pulse power PW of TVS must be greater than the peak pulse power that may occur in the protected circuit.
5. After determining the maximum clamping voltage of the TVS, its peak pulse current should be greater than the transient surge current.
6. For the protection of data interface circuits, it is important to select TVS devices with capacitance C as small as possible.
7. The discreteness of TVS diodes with A is better than that of TVS diodes without A. The model with C in front of TVS diode A indicates a bidirectional TVS diode.
8.Unidirectional TVS diodes are generally used for DC protection, bidirectional TVS diodes are generally used for AC protection, TVS array devices are used for multi-channel protection, and TVS dedicated protection modules are used for high-power protection. In special cases, such as RS-485 and RS-232 protection, bidirectional TVS diodes or TVS arrays can be used.
9. TVS diodes can operate between -55°C and +150°C. If TVS needs to operate at a varying temperature, the reverse leakage current ID increases with increasing temperature, and the power consumption decreases with increasing TVS junction temperature. Therefore, the effect of temperature changes on its characteristics should be considered when selecting TVS.
10. TVS diodes can be used in series or parallel. Serial connection divides voltage, and parallel connection divides current. However, considering the discreteness of TVS, the number of series/parallel connections should be reduced as much as possible when using it.
11. Unipolar or Bipolar - There is often a misunderstanding that bidirectional TVS is used to suppress reverse surge pulses, but this is not the case. Bidirectional TVS is used for AC or positive and negative bidirectional pulses. TVS is sometimes used to reduce capacitance. If the circuit only has positive level signals, then unidirectional TVS is sufficient. The operation of TVS is as follows: during forward surge, TVS is in reverse avalanche breakdown state; during reverse surge, TVS conducts and absorbs surge energy like a forward biased diode. This is not the case in low capacitance circuits. Bidirectional TVS should be selected to protect low capacitance devices in the circuit from reverse surge damage.
TVS diode selection considerations
1) The specification manual only gives the peak absorbed power under a specific pulse width, but the pulse width in the actual circuit varies. You should have a good idea of it and use derating for wide pulses;
2) For the protection of small current load circuits, current limiting resistors should be added consciously;
3) Pay attention to whether the steady-state average power of the TVS diode is within the safe range;
4) Temperature changes must be considered. Normally, TVS diodes operate between -55°C and 150°C. When the temperature in the circuit is relatively high, the rated value must be reduced.
5) The lead length of the TVS transient suppression diode should be relative to the protected circuit.
6) For protection in data interfaces or communication lines, TVS diodes with relatively small capacitance values should be selected as much as possible.
7) Most DC protection circuits use unidirectional TVS tubes, most AC protection circuits use bidirectional TVS tubes, multi-channel protection circuits use TVS array devices, and high-power protection circuits use dedicated protection modules.
8) When using TVS tubes, consider the discreteness of TVS and try to reduce the number of series/parallel connections.
TVS diode characteristics
•Made using semiconductor technology, it has high reliability and no damage limit;
•Glass passivation process, precise on-voltage;
•High transient power, low capacitance, low leakage current, and easy to control clamping voltage;
•Fast response time: usually less than 1.0PS;
•Excellent clamping capability and small breakdown voltage deviation;
•High voltage accuracy. In special applications, higher accuracy can be achieved through process or parameter screening;
•Small size, easy to install;
•One-way and two-way units;
•The transient power can reach 200W-30000W or even higher under 10/1000μs waveform;
• Operating voltage range 3.3V~600V, or even higher;
• Diversified packaging forms, SMD packaging: SOD-123, SMA (DO-214AC), SMB (DO-214AA), SMC (DO-214AB), DO-218AB, etc., direct plug-in packaging: DO-41, DO-15, DO-201, R-6/P-600, etc.;
•Halogen-free, RoHS compliant;
Typical Applications of TVS Diodes
TVS diodes have the advantages of extremely fast response speed, low clamping voltage, and precise voltage. Therefore, they are used in applications with relatively high requirements for protection devices, such as automotive electronics, home appliances, industrial control, lighting, communications, medical and other industries, such as DC power lines, RS485 interfaces, communication power supplies, I/O ports, etc.
- A detailed explanation of common collector
- Understanding the capacitance formula, what are the types of capacitors
- How to convert an inverting amplifier into a summing amplifier?
- Summary of I2C basics: How does I2C communication actually work?
- The unidirectional conduction current of the diode, the diode and its common uses
- What is the difference between MOSFET and BJT? Which one is better between MOSFET and BJT?
- What is an ac to dc transformer in circuit design
- How to identify common mode interference? Methods to eliminate common mode interference
- Why Do Amplifier Fuses Blow? How Do You Prevent Amplifier Fuses from Blowing?
- Datasheet/Pinout/Technical Specifications of LMC555
- 555 square wave oscillation circuit
- 555 photo exposure timer circuit diagram
- Introducing the CD4013 washing machine timer circuit diagram
- Simple level conversion circuit diagram
- 555 electronic guide speaker circuit diagram for blind people
- Circuit diagram of disconnection alarm composed of 555
- Analog circuit corrector circuit diagram
- color discrimination circuit
- Color sensor amplification circuit
- Level indication circuit








 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号